Understanding Approval Routing for Applications
Approval routing is the process of directing access requests to appropriate approvers based on organizational policies and governance requirements. Rather than granting access automatically when users request permissions, approval routing ensures that authorized stakeholders review and approve requests before access is granted. This provides oversight, enforces segregation of duties, supports compliance requirements, and ensures that access aligns with organizational policies.
Traditional approval routing often relies on static approver assignments—specific individuals or groups designated to review all requests of a certain type. While straightforward to implement, static routing lacks flexibility and cannot adapt to the context of individual requests. Policy-Based Access Control (PBAC) approval routing in EmpowerID provides a dynamic, context-driven alternative that routes requests to appropriate approvers based on the specific attributes and conditions of each request.
The Challenge with Static Approval Routing
Static approval routing assigns fixed approvers to review access requests. For example, all requests for financial system access might route to a single Financial Systems Manager, or all requests for a specific application might route to the IT department. This approach is simple but presents several limitations:
Lack of Context Awareness - Static routing cannot account for the specific details of a request. A request for read-only access to public financial reports receives the same routing as a request for full administrative access to confidential financial data, even though these require different levels of scrutiny.
Bottlenecks and Scalability Issues - When all requests route to a small number of approvers, those individuals become bottlenecks. In large organizations, this can lead to significant delays and overwhelmed approvers who cannot provide meaningful review.
Organizational Complexity - As organizations grow more complex—spanning multiple regions, business units, and regulatory jurisdictions—static routing cannot reflect this complexity. A request for access to European data should ideally route to approvers with European operations knowledge and regulatory expertise, not to a generic global approver.
PBAC approval routing addresses these limitations by evaluating request attributes dynamically to determine the most appropriate approvers for each specific request.
How PBAC Enables Dynamic Approval Routing
PBAC approval routing leverages Field Types—the same attribute-based mechanism used in authorization policies—to make intelligent routing decisions. When users request access, they may specify attributes such as region, department, data classification, or project. PBAC evaluates these attributes in real time to determine which approvers have the appropriate authority and context to review the request.
PBAC approval routing refines the approval process by tying approver selection directly to request context. When users request access to application data, they may specify attributes that influence who should approve the request. PBAC evaluates these attributes in real time to determine the right approvers.
For example, a request for financial data access that specifies "North America" as the region routes to finance team approvers in North America, while a request specifying "Europe" routes to European finance approvers. The same policy structure adapts to route requests appropriately based on the attributes users select or that are derived from the request context.
This dynamic approach ensures that approvals are policy-driven, context-aware, and aligned with organizational rules and security requirements. Approvers receive requests that are relevant to their domain of responsibility, improving both the quality of approval decisions and the efficiency of the approval process.
For more information on Field Types and how they enable attribute-based decisions, see Understanding Field Types in EmpowerID PBAC.
Approval Routing Architecture
Understanding how approval routing works in EmpowerID requires familiarity with several key components that work together to process and route access requests.
Access Request Policy and Approval Policy
At the heart of approval routing are two policy types that define how requests are processed and evaluated:
Access Request Policy - This policy governs how incoming access requests are initially processed. The Access Request Policy determines whether a request requires approval, what information must be collected, and which Approval Policy should be invoked to handle the approval workflow.
Approval Policy - This policy defines the specific approval workflow steps required for a request. The Approval Policy specifies the types of approvers who must review the request and the logic for identifying those approvers. For PBAC-based approval routing, the Approval Policy includes resolver rules that dynamically determine approvers based on request attributes.
Together, these policies form the foundation of the approval process, ensuring that requests flow through a structured and consistent pipeline from submission through approval to fulfillment.
Visualizing the Approval Framework
The following diagram illustrates how requests move from resources, through the Access Request Policy and Approval Policy, and finally to the appropriate approvers:
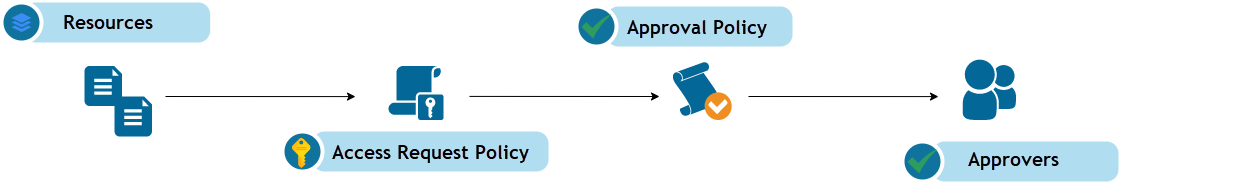 Figure: Relationship Between Resources, Access Request Policy, Approval Policy, and Approvers
Figure: Relationship Between Resources, Access Request Policy, Approval Policy, and Approvers
In this diagram, the resources—representing the rights or data a user requests—flow into the Access Request Policy. This policy invokes the Approval Policy to determine the approval steps and logic. From there, the process identifies and routes to the appropriate approvers, ensuring that only authorized individuals evaluate and grant access.
Approval Methods for Application Rights
EmpowerID supports multiple approval routing methods that vary in flexibility and complexity. Organizations can choose the method that best aligns with their governance requirements and organizational structure.
Static Approvers
Static approvers use a fixed set of individuals, groups, or roles to review requests. Every request of a given type routes to the same approvers regardless of request details or context.
When to use: Static approvers work well for simple scenarios with centralized decision-making authority, or when the approval authority is clearly defined and does not vary based on request attributes.
Limitations: This method lacks flexibility and cannot adapt to organizational complexity or request context.
RBAC-Based Approvers
RBAC-based approvers derive approvers from organizational roles defined in EmpowerID. Requests route to users who hold specific Management Roles, Business Roles and Locations, or group memberships.
When to use: RBAC-based routing provides more adaptability than static approvers while remaining straightforward to configure. It works well when approval authority aligns with organizational roles that are already modeled in EmpowerID.
Limitations: While more flexible than static routing, RBAC-based approvers are still relatively broad and cannot account for fine-grained request attributes like data classification or regional scope.
PBAC Approvers
PBAC approvers identify approvers dynamically based on Field Types and their values. This is the most flexible method and is the recommended approach for PBAC-enabled applications.
When to use: Use PBAC approvers when approval decisions should vary based on request attributes such as region, department, data classification, or project. This method allows organizations to tailor approvals to each request's context, ensuring that the right stakeholders review each request.
Benefits: PBAC approval routing scales naturally with organizational complexity, eliminates routing bottlenecks by distributing approval responsibility, and ensures approvers have relevant context for the requests they review.
PBAC Approver Resolver Rule
The PBAC Approver Resolver rule is the mechanism that operationalizes context-sensitive approval selection. This resolver evaluates Field Types and their values associated with access requests to identify users or groups with the corresponding approval rights.
Consider a Field Type such as "Region," with values like "North America," "Europe," and "Asia." For each application right that requires approval, administrators can define approval rights tied to these regional values. When a user requests access and selects "North America" as the region, the PBAC Approver resolver examines which users hold the approval right for North America and routes the request to them.
When a request involves multiple Field Type values, EmpowerID splits the request into individual items—one per value. The resolver then determines which approvers hold the relevant approval rights for each item, ensuring targeted and appropriate review for each component of the request.
This resolver-based approach ensures that approval routing adapts automatically to new regions, departments, data classifications, or other organizational attributes as they are added to the system. The policies and resolver logic remain stable while the routing decisions adjust to current organizational structure.
How PBAC Approval Routing Works
To understand how PBAC approval routing operates in practice, consider the complete workflow from request submission through approval:
Configuration Phase
Administrators define or customize a PBAC Access Request Policy and associate application rights with a PBAC Approval Policy. Field Types are configured to support condition-aware routing, and approval rights are granted to users or groups for specific Field Type values. For example, approval rights for "North America" financial data might be granted to North American finance managers.
Request Submission
A user requests access to specific application rights and selects relevant Field Type values during the request. If the request involves multiple values—such as requesting access to both North America and Europe regions—EmpowerID creates separate request items for each value.
Resolver Execution
The PBAC Approver resolver examines each request item, evaluates the Field Type values associated with it, and compares these against configured approval rights. The resolver identifies which users or groups hold approval rights matching the request attributes.
Approval Routing
Request items are routed to their respective approvers based on the resolver's determination. Each approver receives requests relevant to their domain of responsibility—such as regional scope, departmental authority, or data classification expertise. Approvers evaluate requests based on their knowledge of business requirements and organizational policy, making informed decisions about whether to approve or deny access.
Example: Regional Financial Data Request
To illustrate this workflow, consider a user requesting access to view financial reports. During the request, the user specifies two regions: "North America" and "Europe."
EmpowerID splits this into two request items. The PBAC Approver resolver evaluates each item's regional attribute and identifies:
- North American finance managers hold approval rights for "North America"
- European finance managers hold approval rights for "Europe"
The North America item routes to North American finance managers, while the Europe item routes to European finance managers. Each approval team reviews only the portion relevant to their region. If North American managers approve but European managers deny, the user receives access to North American financial reports but not European reports.
This example demonstrates how PBAC approval routing ensures that the right stakeholders—those with relevant context and authority—review each request component.
Summary
PBAC approval routing in EmpowerID provides a dynamic, context-driven framework for governing application access requests. By leveraging Field Types—the same attribute-based mechanism used in authorization policies—PBAC routes requests to appropriate approvers based on request attributes such as region, department, data classification, or project.
This approach addresses the limitations of static approval routing by ensuring that approvers receive requests relevant to their domain of responsibility. It scales naturally with organizational complexity, eliminates approval bottlenecks, and ensures that approval decisions are made by stakeholders with appropriate context and authority.
Through the PBAC Approver resolver rule, organizations can implement sophisticated approval workflows that adapt automatically as organizational structures evolve. The same resolver logic continues to work correctly as new regions, departments, or data classifications are added, requiring only that approval rights be granted to appropriate approvers for new attribute values.
PBAC approval routing demonstrates how the integration of RBAC structures (roles, rights, organizational hierarchy) with ABAC principles (Field Types, dynamic evaluation) extends beyond authorization decisions to encompass the entire access governance lifecycle, including request submission, approval routing, and access fulfillment.