Create Azure AD PowerShell Workflow
This tutorial demonstrates how to create and publish an Azure AD PowerShell workflow using Workflow Studio. The workflow executes PowerShell cmdlets against Azure AD and displays results in a grid format.
Overview
You will build a workflow that:
- Uses AzXPowerShellActivity to execute PowerShell commands in the Azure AD microservice
- Retrieves DisplayName, Mail, and ObjectId for the top 50 Azure AD users
- Displays results using DynamicPowershellResultsGrid
The workflow executes this PowerShell command:
Get-AzureADUser -Top 50 | Select DisplayName, Mail, ObjectId | ConvertTo-Json
Prerequisites
- Azure AD account store configured in EmpowerID
- Permissions to execute Azure AD PowerShell cmdlets
For detailed information about PowerShell activities and their properties, see PowerShell Activity Concepts.
Create the Workflow
Step 1: Initialize Workflow
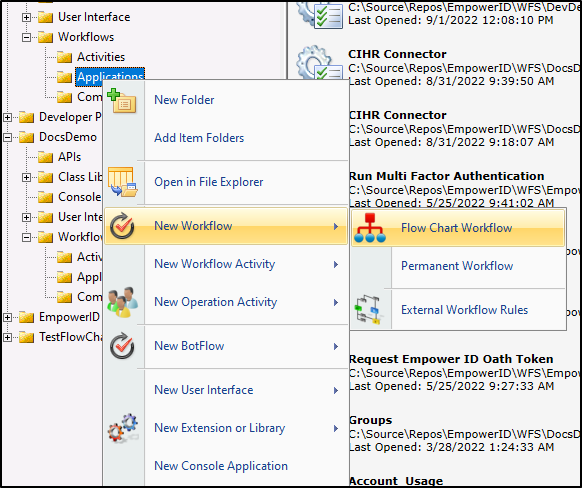
- In Solution Explorer, right-click the Package node and select New Workflow > Flow Chart Workflow.
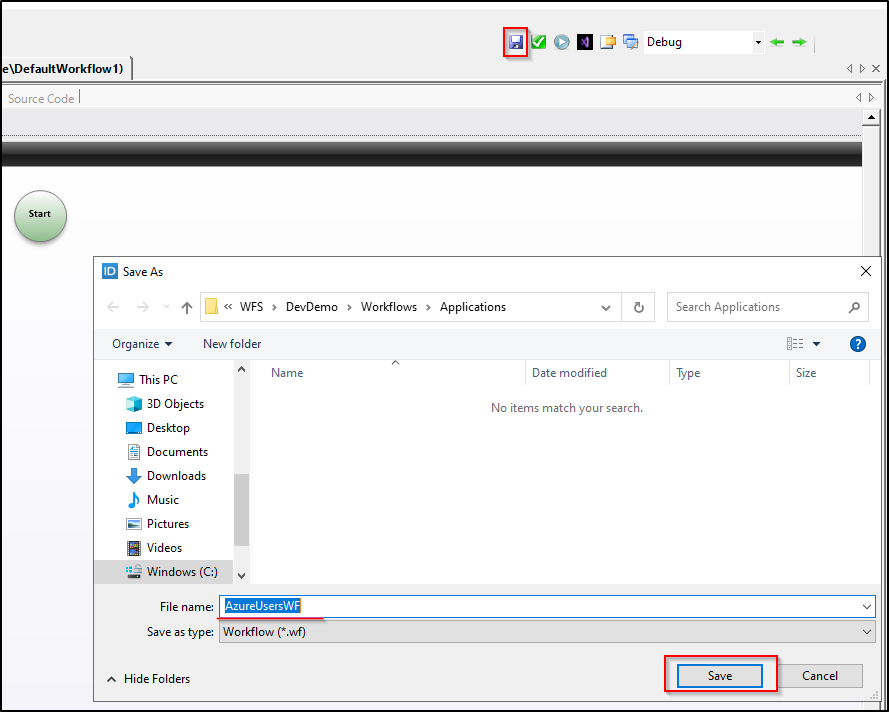
- Save the workflow with a descriptive name (e.g., "AzureUsersWF").
Step 2: Add AzXPowerShellActivity
- From the Activities tab, search for AzXPowerShellActivity.
- Drag the activity to the designer window.
- In the Properties tab, set Name to a meaningful value (e.g., "GetADUsersCmdlet").

Step 3: Configure PowerShell Command
-
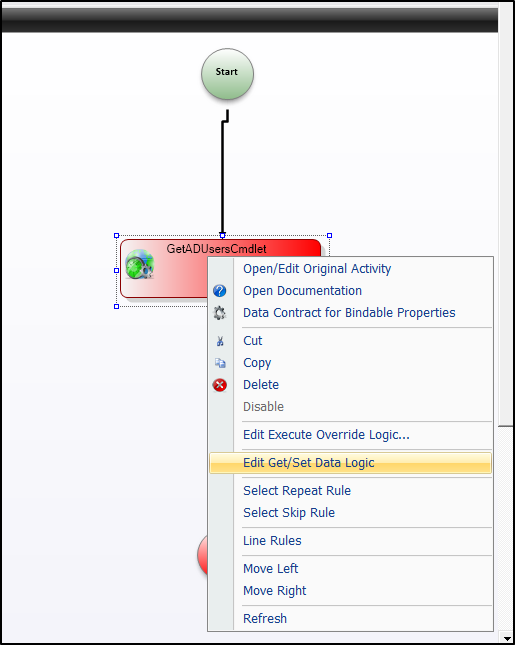
Right-click the activity and select Edit Get/Set Data logic.
-
Add the PowerShell library reference:
using PS = TheDotNetFactory.Framework.PowerShell; -
Implement the SetDataCode method:
public virtual void SetDataCode(uni.WorkflowExecutor context, uni.IActivity activity)
{
try
{
// Create PowerShell command
PS.PSCommand cmd = new PS.PSCommand();
cmd.IsScript = true;
cmd.CommandText = "Get-AzureADUser -Top 50 | Select DisplayName, Mail, ObjectId | ConvertTo-Json";
var commands = new List<PS.PSCommand>();
commands.Add(cmd);
// Configure activity properties
this.CurrentWorkflow.GetADUsersCmdlet.PSServiceType = AzPowerShellType.AzureAD;
this.CurrentWorkflow.GetADUsersCmdlet.AccountStoreID = 2615; // Replace with your Azure AD account store ID
this.CurrentWorkflow.GetADUsersCmdlet.Commands = commands;
this.CurrentWorkflow.GetADUsersCmdlet.RestrictDelayToSameServer = true;
this.CurrentWorkflow.GetADUsersCmdlet.EnablePassiveResultsHandling = false;
this.CurrentWorkflow.GetADUsersCmdlet.MaxWaitLoopCount = 10;
TdnfTrace.Current.TraceData(TraceEventType.Verbose, 411,
"Starting to execute command: " + cmd.CommandText);
}
catch(Exception ex)
{
TdnfTrace.Current.TraceData(TraceEventType.Error, 411,
"Error executing PowerShell command: " + ex.Message);
throw; // Re-throw to allow workflow error handling
}
}Key Configuration Properties:
Property Value Description PSServiceTypeAzPowerShellType.AzureADSpecifies Azure AD as the PowerShell service target AccountStoreIDYour account store ID Identifies the Azure AD account store for authentication RestrictDelayToSameServertrueEnsures execution on the same server EnablePassiveResultsHandlingfalseDisables passive result collection MaxWaitLoopCount10Maximum polling attempts for command completion cautionReplace
2615with your Azure AD account store ID. Find this value in Object Administration > Account Stores by locating your Azure AD account store and noting its ID.
Step 4: Add Results Grid
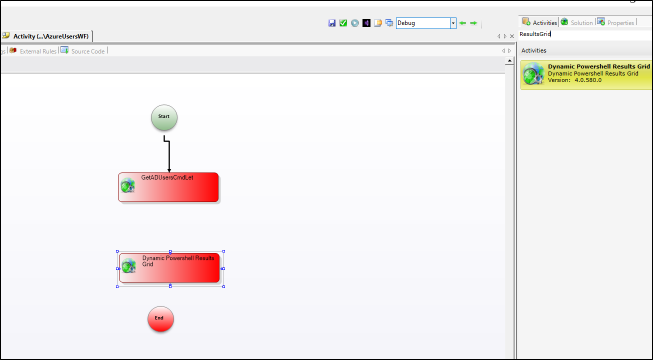
- Search for DynamicPowershellResultsGrid in the Activities tab.
- Drag the activity to the designer.
- Set Name to "ShowUserResults" in the Properties tab.
Step 5: Connect Activities and Configure Results
-
Right-click AzXPowerShellActivity and select Edit Get/Set Data logic.
-
Implement the GetDataCode method to pass results to the grid:
public virtual void GetDataCode(uni.WorkflowExecutor context, uni.IActivity activity)
{
// Transfer PowerShell results to the grid display
this.CurrentWorkflow.ShowUserResults.Result = this.CurrentWorkflow.GetADUsersCmdlet.Results;
} -
Connect all activities in the workflow designer.
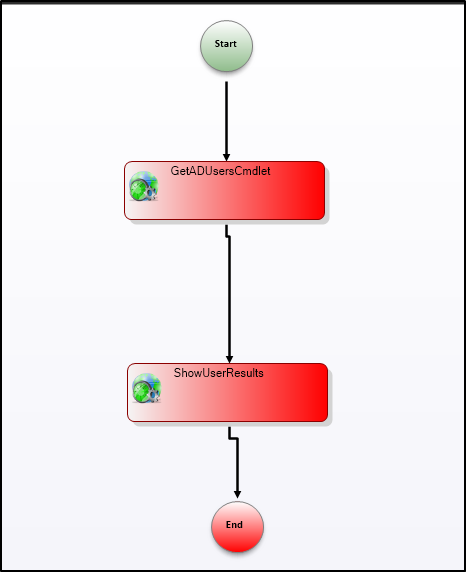
Step 6: Compile
Click the Compile icon to compile the workflow code. Address any compilation errors before proceeding.
Publish the Workflow
- Click the Compile and Publish button in the Workflow Studio toolbar.
- In the Publish Workflow wizard that appears, click the Next button.
- Select the host server and click Next.
- Click Next again to begin compiling the workflow. Upon a successful compilation, Workflow Studio publishes the workflow.
- Select Yes when prompted to restart one or more services.
- In the Active Services window that appears, make sure the EmpowerID Web Role Service is selected and click Restart.
- Click No when prompted to restart Workflow Studio.
Verify Workflow Execution
- Log in to the EmpowerID portal.
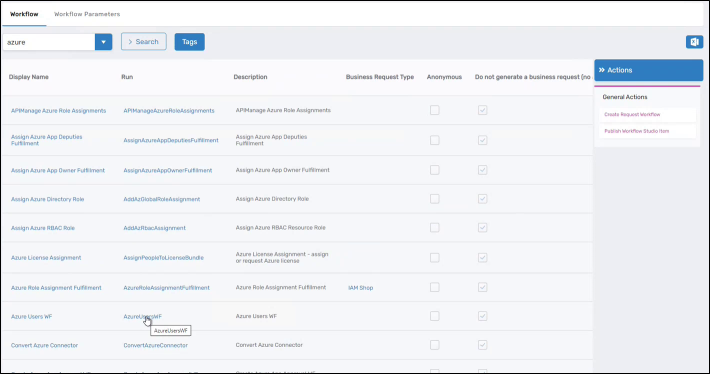
- Navigate to Low Code/No Code Workflows > Low Code Workflows.
- Locate your published workflow and click the workflow name in the Run column.
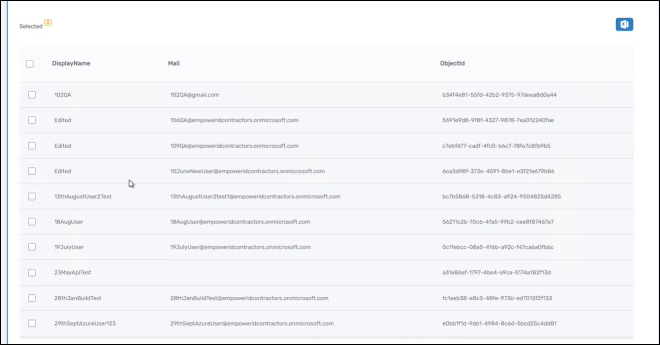
- Verify the grid displays Azure AD user data with DisplayName, Mail, and ObjectId columns.
Related Topics
- PowerShell Activity Concepts - Learn about PowerShell activity properties and configuration
- Create MSOnline PowerShell Workflow - Build workflows for Microsoft Online services